Abstract
Introduction
Lymphodepletion chemotherapy followed by infusion of T cells engineered to express a CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) has shown remarkable efficacy in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) CD19+ B-cell malignancies, with high response rates reported in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Durable responses have been observed in a subset of pts, but the factors associated with these long-term remissions have not been identified. We studied adults with R/R CD19+ B-cell NHL treated with cyclophosphamide and fludarabine lymphodepletion followed by infusion of 2 x 106 CD19 CAR-T cells/kg, and identified factors before and after CAR-T cell infusion that are associated with progression-free survival (PFS).
Methods
We conducted a phase 1/2 open-label clinical trial (NCT01865617) with the primary objective of evaluating the feasibility and safety of infusing a defined composition of CD4+ and CD8+ CD19 CAR-T cells after lymphodepletion chemotherapy in pts with R/R CD19+ B-cell malignancies. Best responses are reported according to the Lugano criteria (Cheson, JCO 2014). PFS was defined as the time from CAR-T cell infusion until disease progression or death, without censoring for new therapy. Logistic regression and penalized Cox regression multivariable modeling using elastic net were performed for analysis of response and PFS, respectively.
Results
Characteristics of the 57 pts in the study are shown in Table 1. One patient with incomplete response assessment was excluded. For the 56 remaining pts, the best overall response rate (ORR) without additional therapy was 57% (95% confidence interval [CI], 43-70%), with 48% achieving complete remission (CR; 95% CI, 35-62%). Most pts with partial response (PR) or stable disease (SD) after initial restaging at 4 weeks after CAR-T cell infusion received new therapy (11 of 15, 73%). All pts with PR/SD on initial restaging who did not receive additional therapy after CAR-T cells (n = 4) subsequently achieved CR. The duration of persistence of CAR-T cells was longer in pts who did not receive new therapy (15.7 vs. 5.3 months; P = .06).
Eight of 9 pts with indolent histology achieved CR (89%; 95% CI, 51-99%). For the 47 pts with aggressive NHL, the best ORR was 51% (95% CI, 36-66%), with 40% (95% CI, 27-56%) achieving CR. Among aggressive NHL subtypes, pts with DLBCL (n = 28) had best ORR and CR rates of 50% (95% CI, 33-67%) and 43% (95% CI, 25-63%), respectively. In pts with aggressive lymphoma, multivariable analysis showed that the probability of achieving CR was independently associated with a lower pre-lymphodepletion serum LDH concentration (P = .003) and greater increase in serum MCP-1 concentration from a pre-lymphodepletion timepoint to immediately before CAR-T cell infusion (P = .01).
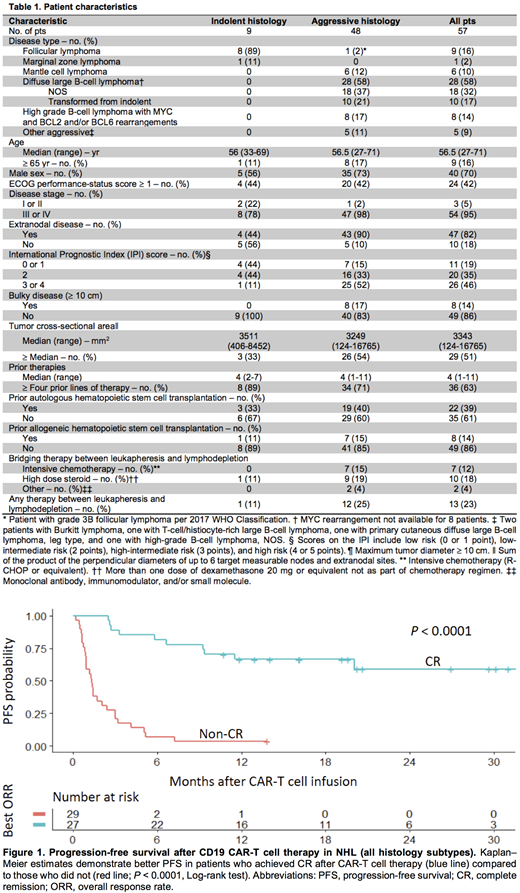
Analysis of pts with all histologic subtypes showed that those achieving CR had better PFS and overall survival (OS) compared to those who did not achieve CR (median PFS: CR, not reached; non-CR, 1.35 month; Figure 1). In pts achieving CR, after a median follow-up of 20.2 months (range 2.5-32.4 months), the 24-month probabilities of PFS and OS were 59% (95% CI, 41-84%) and 79% (95% CI, 64-97%), respectively. No pts with indolent NHL who achieved CR (n = 8) have relapsed with a median follow-up of 14.5 months (range, 10.7-30.1 months). For pts with aggressive lymphoma who achieved CR, after a median follow-up of 26.9 months (range, 2.5-32.4 months), the median PFS was 20.0 months (95% CI, 9.2-not reached), and 24-month probabilities of PFS and OS were 46% (95% CI, 28-76%) and 72% (95% CI, 54-96%), respectively.
In aggressive NHL, multivariable analysis suggested that, in addition to being associated with the probability of achieving CR, serum LDH and MCP-1 concentration also impacted the probability of longer PFS. The model found that lower pre-lymphodepletion serum LDH (P = .0004) and higher serum MCP-1 peak after CAR-T cell infusion (P = .05), along with higher serum IL-7 (P = .02) and lower serum IL-18 (P = .02) concentrations before lymphodepletion were independently associated with better PFS. Similar findings were obtained after multivariable analysis was performed only in those who had achieved CR.
Conclusion
CR after CD19 CAR-T cell therapy appears to be a strong predictor of PFS in adult pts with B-cell NHL. Identification of additional factors associated with better PFS might guide future management strategies for pts achieving CR after CD19 CAR-T cell therapy.
Hirayama:DAVA Oncology: Honoraria. Hay:DAVA Oncology: Honoraria. Li:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Lynch:Incyte: Research Funding; Johnson Graffe Keay Moniz and Wick LLP: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Rhizen Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Till:Mustang Bio: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Kiem:Homology Medicine: Consultancy; Rocket Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Magenta: Consultancy. Ramos:Seattle Genetics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Shadman:Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Mustang Biopharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy; Beigene: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Qilu Puget Sound Biotherapeutics: Consultancy. Cassaday:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Other: Spouse Employment, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Acharya:Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Teva: Honoraria. Riddell:Cell Medica: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; NOHLA: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy. Maloney:GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding; Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Janssen Scientific Affairs: Honoraria. Turtle:Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Juno Therapeutics / Celgene: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Nektar Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Eureka Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Precision Biosciences: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Caribou Biosciences: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Aptevo: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal